Updated Nov 16
Table of Contents
- Smoking & Heart Disease: The Deadly Connection
- Facts about smoking and heart disease
- What Is Heart Disease and Stroke?
- How does smoking change the heart and blood vessels?
- Quitting Smoking and Avoiding Secondhand Smoke
- What are the risks of secondhand smoke?
- Does smoking increase your high blood pressure risk?
- 10 of the Worst Diseases Smoking Causes
- Are other forms of tobacco safer?
- How does smoking affect your body?
- Marijuana Linked to Heart Disease; Supplement May Mitigate Risk, Study Reports
- THC and inflammation
- How does chewing tobacco affect your health?
- Is Vaping Safer Than Smoking a Cigarette?
- How are health problems from tobacco diagnosed?
- What other conditions may be caused or worsened by tobacco?
- Diabetes and Heart Disease: A Deadly Connection
Smoking & Heart Disease: The Deadly Connection
Smoking and heart disease have a deadly connection. When you smoke, it not only affects your lungs but also takes a toll on your heart and blood vessels. The harmful chemicals contained in tobacco smoke can cause serious damage to your cardiovascular system.
One of the ways smoking affects the heart is by increasing blood pressure. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to elevated blood pressure. This puts extra strain on the heart, making it work harder than it should. Additionally, smoking can also increase heart rate, making the heart pump faster, which can be detrimental to its health.
Furthermore, smoking changes the way blood flows through the blood vessels. It promotes the development of fatty plaques in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which can lead to blockages and reduce blood supply to the heart. This increases the risk of coronary heart disease, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular problems.
Moreover, smoking increases the risk of blood clots, which can lead to stroke. The chemicals in cigarette smoke make the blood stickier and more prone to clotting, putting smokers at a higher risk for ischemic strokes.
In addition to the physical effects on the heart and blood vessels, smoking is also associated with an increased risk of depression. Studies have shown a link between smoking and mental health, with smokers being more likely to experience depressive symptoms.
SOURCE: Puffing away sadness. Harvard Health Publishing.
In summary, smoking not only damages the lungs but also has severe repercussions on the heart and blood vessels. The increased blood pressure, reduced blood flow, and higher risk of blood clots and stroke highlight the serious risks smokers face when it comes to heart disease. It’s important to understand the damaging effects of smoking and make efforts to quit in order to protect your heart and overall health.
Facts about smoking and heart disease
Smoking and heart disease have a deadly connection, with key facts highlighting the grave risks involved. For one, smoking significantly increases the risk for heart disease. Smokers are two to four times more likely to develop heart disease compared to non-smokers.
SOURCE: Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease. Johns Hopkins Medicine.
SOURCE: Health Effects of Cigarette Smoking. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This correlation is concerning considering that heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and a significant number of those deaths are directly smoking-related.
SOURCE: Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
But the dangers don’t stop there. Smokers also face a higher risk of stroke. As previously noted, this is due to the chemicals in cigarette smoke making the blood stickier, which increases the likelihood of blood clots forming. As a result, smokers are twice as likely to suffer a stroke compared to non-smokers.
SOURCE: Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Drug Facts. National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
SOURCE: How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: What It Means to You. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health.
It’s not just the heart and brain that are at risk. Smoking is also associated with an increased vulnerability to various lung diseases. The risk for lung cancer is a staggering 15-30 times higher in smokers compared to non-smokers.
SOURCE: What Are the Risk Factors for Lung Cancer? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Additionally, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes diseases like emphysema and chronic bronchitis, also affects a significant number of smokers.
SOURCE: Wheaton, A. G., Liu, Y., Croft, J. B., VanFrank, B., Croxton, T. L., Punturieri, A., Postow, L., & Greenlund, K. J. (2019). Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Smoking Status — United States, 2017. MMWR, 68(24), 533–538.
SOURCE: Terzikhan, N., Verhamme, K. M. C., Hofman, A., Stricker, B. H., Brusselle, G. G., & Lahousse, L. (2016, March 5). Prevalence and incidence of COPD in smokers and non-smokers: the Rotterdam Study. European Journal of Epidemiology, 31(8), 785-792.
The facts are clear: smoking is a major threat to both heart health and overall well-being. Quitting smoking is the best step one can take to reduce these risks and improve their quality of life.
Check out this timeline, showing 8 benefits to quitting smoking:
What Is Heart Disease and Stroke?
Heart disease and stroke are two of the most common types of cardiovascular diseases, which affect the heart and the blood vessels. Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that involve the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmia, and heart valve problems. Stroke, on the other hand, occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, leading to damage to brain cells and potential long-term disabilities.
A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, is a specific type of heart disease that occurs when there is a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This blockage can be caused by a blood clot or a buildup of plaque in the arteries. When the blood flow is restricted, the heart muscle may be damaged, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms.
SOURCE: Heart Attack – What Is a Heart Attack?. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI).
Watch this video to learn about heart attack symptoms and how they may differ from person to person:
Stroke, often referred to as a “brain attack,” happens when a blood vessel carrying oxygen-rich blood to the brain is either blocked by a clot (ischemic stroke) or ruptures and bleeds (hemorrhagic stroke). As a result, the brain cells in the affected area are deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to tissue damage and potentially severe neurological complications.
SOURCE: Stroke – What Is a Stroke?. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI).
Both heart disease and stroke can have life-threatening consequences and require immediate medical attention. It is essential to understand the risk factors and take steps to maintain heart health, such as quitting smoking, staying physically active, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing other underlying health conditions. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and stroke and lead a longer, healthier life.
Here are 10 ways you can be more proactive about your heart health:

How does smoking change the heart and blood vessels?
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the heart and blood vessels, both immediately and in the long term. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke can cause immediate changes in the body, such as an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. These changes put added stress on the heart, which can lead to a higher risk of heart disease.
SOURCE: Smoking and Your Heart – How Smoking Affects the Heart and Blood Vessels. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI).
It is important to note that these effects are not limited to active smokers. Secondhand smoke exposure can also have damaging effects on the heart and blood vessels. The harmful chemicals in tobacco products can be inhaled by those in close proximity to smokers, increasing their risk of heart disease as well.
To protect your heart health, quitting smoking is crucial. By quitting, you can reduce your blood pressure, improve blood flow, and lower your risk of heart disease. Additionally, it is important to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke to minimize the negative impact on your heart and blood vessels. Remember, every step towards a smoke-free life is a step towards better heart health.
Quitting Smoking and Avoiding Secondhand Smoke
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke are crucial steps in reducing the risk of heart disease. Not only is smoking the leading cause of premature, preventable death, but it also harms nearly every organ in the body. Heart disease, along with cancer, stroke, lung disease, and worsened asthma symptoms, are just some of the health problems caused by smoking.
When it comes to heart health, smoking is particularly harmful. As noted previously, the toxins in cigarette smoke can damage the lining of the blood vessels, leading to the development of plaque and narrowing of the arteries. This reduces blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
But again, it’s not just smokers who are at risk. Secondhand smoke is equally harmful. Nonsmokers exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to develop heart disease, lung cancer, and other respiratory problems. In fact, exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk of heart disease by 25-30%.
SOURCE: Secondhand Smoke (SHS) Facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
By quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of heart disease and other serious health conditions. It’s never too late to quit smoking and improve your heart health. Speak to a healthcare professional for guidance and support on your journey towards a smoke-free life.
What are the risks of secondhand smoke?
Secondhand smoke poses significant risks to both adults and children. Breathing in the toxic chemicals emitted by tobacco products can have serious health consequences, including an increased risk of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, respiratory conditions, and other related health problems.
Exposure to secondhand smoke has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, even among those who do not smoke themselves. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can linger in the air for hours, and when inhaled, they can damage the cells in the lungs, leading to the development of cancer over time.
In addition to lung cancer, exposure to secondhand smoke can also contribute to the development of heart disease. As previously noted, the chemicals in tobacco smoke can enter the bloodstream, causing damage to the blood vessels and increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, where the arteries become narrowed and hardened. This can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Respiratory conditions, such as asthma, can also be worsened by exposure to secondhand smoke. The irritants in tobacco smoke can trigger asthma attacks and make breathing more difficult for those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Symptoms associated with secondhand smoke exposure include eye and throat irritation, persistent coughing, chest discomfort, bronchitis, and an increased susceptibility to respiratory infections.
It is important to protect ourselves and our loved ones from the risks of secondhand smoke by creating smoke-free environments and supporting policies that restrict smoking in public places. By taking these steps, we can help reduce the harmful effects of secondhand smoke and improve the overall health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Does smoking increase your high blood pressure risk?
SOURCE: Primatesta, P., Falaschetti, E., Gupta, S., Marmot, M. G., & Poulter, N. R. (2001). Association Between Smoking and Blood Pressure: Evidence From the Health Survey for England. Hypertension, 37(2), 187-193.
Smoking and high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, are a dangerous combination. Research has shown that smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly increase the risk of developing plaque buildup in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
SOURCE: Barnoya, J., & Glantz, S. A. (2005). Cardiovascular Effects of Secondhand Smoke: Nearly as Large as Smoking. Circulation, 111(20), 2684–2698.
One of the ways smoking affects blood pressure is by causing a temporary increase with each cigarette. The nicotine in cigarettes stimulates the release of adrenaline, which in turn raises blood pressure. Over time, this repeated increase in blood pressure can contribute to the development of hypertension.
Furthermore, smoking also increases the risk factors for high blood pressure. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lining of the blood vessels, making them less elastic and more prone to plaque buildup. As plaque accumulates in the arteries, they become narrower, making it harder for blood to flow freely, and potentially leading to high blood pressure.
It’s important to note that quitting smoking has numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of high blood pressure and other cardiovascular diseases. By quitting smoking, individuals can significantly improve their heart health and overall well-being.
If you are a smoker and concerned about your blood pressure, it is vital to take steps towards quitting, as well as adopting a healthier lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques. Prioritizing your health and making positive changes can greatly reduce the risk of complications associated with high blood pressure.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD OUR HEART HEALTH ACCOUNTABILITY TRACKER
10 of the Worst Diseases Smoking Causes
SOURCE: Fast Facts and Fact Sheets. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Smoking is not just a bad habit; it can have devastating consequences for your health. In fact, smoking is the leading cause of preventable diseases and premature death worldwide. The list of diseases caused by smoking is long, but here are ten of the worst ones:
1. Lung Cancer: Smoking is the primary cause of most cases of lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the cells in the lungs, leading to the formation of cancerous tumors.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): This progressive lung disease includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking irritates and inflames the airways, causing difficulty breathing and increased mucus production.
3. Heart Disease: Smoking is a major contributor to heart disease, which includes conditions like coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and heart failure. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the heart muscle and blood vessels, leading to decreased blood supply to the heart.
4. Stroke: Smoking increases the risk of stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked or interrupted. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause the blood vessels in the brain to narrow or clot, leading to a stroke.
5. Asthma: Smoking irritates and inflames the airways in the lungs, making them more susceptible to asthma attacks. It can worsen asthma symptoms and decrease lung function.
6. Reproductive Effects in Women: Smoking can cause serious reproductive issues in women, including decreased fertility, complications during pregnancy, and an increased risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
7. Premature and Low Birth-Weight Babies: Smoking during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of delivering premature and low birth-weight babies. These babies are at a higher risk of health problems and developmental issues.
8. Diabetes: Smokers have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Smoking can also worsen diabetes complications, such as heart and kidney disease.
9. Blindness and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Smoking damages the blood vessels in the eyes and increases the risk of vision loss and blindness. It is also a major risk factor for age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
10. Various Types of Cancer: In addition to lung cancer, smoking is linked to several other types of cancer, including mouth, throat, esophageal, bladder, kidney, pancreatic, and cervical cancer.
These ten diseases only scratch the surface of the health risks associated with smoking. It’s crucial to prioritize your health and quit smoking to reduce your risk of these serious conditions. If you need help quitting smoking, reach out to healthcare professionals who can provide guidance and support.
SOURCE: 10 of the Worst Diseases Smoking Causes. American Lung Association.
Are other forms of tobacco safer?
While smoking cigarettes is widely known to be extremely harmful to health, many people wonder if other forms of tobacco are safer alternatives. Unfortunately, the answer is not as positive as one might hope. Let’s take a closer look at some of these alternatives and their associated risks.
Cigar smoking, for instance, carries similar risks to cigarette smoking. Despite the perception that cigars are less harmful, they actually contain many of the same toxic chemicals as cigarettes. The smoke from cigars can still lead to various types of cancer, including lung, throat, and esophageal cancer.
Chewing tobacco and smokeless tobacco products also pose significant dangers. These products contain almost 30 cancer-causing chemicals. Prolonged use of chewing tobacco can lead to various oral health problems, including gum disease, tooth decay, and even oral cancer.
In recent years, e-cigarettes, also known as vapes, have gained popularity. While some people view them as potential alternatives to traditional smoking, there are still uncertainties regarding their safety. E-cigarettes often contain high levels of nicotine, which can be addictive and harmful to the developing brains of young people. Furthermore, there is concern that e-cigarettes may act as a gateway to other forms of nicotine use.
Ultimately, it is important to understand that while other forms of tobacco may appear to be safer than cigarettes, they still carry significant health risks. Quitting tobacco use altogether is the best way to safeguard your health and reduce the risk of developing serious medical conditions.
SOURCE: Smokeless tobacco products. Mayo Clinic.
SOURCE: Is Any Type of Tobacco Product Safe? American Cancer Society.
How does smoking affect your body?
Smoking and its harmful effects on the body cannot be underestimated. The act of smoking introduces thousands of chemicals and carcinogens into the body, wreaking havoc on every organ. From the moment smoke is inhaled, it begins to damage the respiratory system, leading to conditions such as bronchitis, emphysema, and eventually, lung cancer.
But the harm doesn’t stop there. Smoking significantly decreases lifespan, with smokers living an average of 10 years less than non-smokers. It also affects pregnant women and their unborn babies, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy, birth defects, and even low birth weight.
SOURCE: Diseases and Death. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
SOURCE: Smoking, Pregnancy, and Babies. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The consequences of smoking extend beyond the respiratory system and pregnancy. It increases the risk of gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss and oral health problems. Furthermore, smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and increasing the risk of illness.
Smoking is also linked to a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
Let’s not forget the impact of chewing tobacco. By chewing or using smokeless tobacco products, users become addicted to nicotine, just like with smoking. Chewing tobacco also increases the risk of oral cancers and gum disease, leading to a host of oral health problems.
SOURCE: Smokeless Tobacco: Health Effects. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As one would expect, smoking has severe consequences for our bodies. It not only damages our organs, but it also affects our overall health and decreases our lifespan. Quitting smoking is the best decision one can make for their well-being and that of those around them.
Marijuana Linked to Heart Disease; Supplement May Mitigate Risk, Study Reports
In a recent study conducted by Stanford Medicine, researchers have found a concerning link between marijuana use and heart disease. The study revealed that individuals who use marijuana regularly may face an increased risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
SOURCE: Frequent Marijuana Use Linked to Heart Disease. American College of Cardiology.
SOURCE: Conger, K. (2022, April 29). Marijuana linked to heart disease; supplement may mitigate risk, study reports. Stanford Medicine News Center.
The culprit behind this connection is THC, the psychoactive compound found in marijuana. THC has been found to cause inflammation in the blood vessels, leading to the development of cardiovascular issues. This inflammation can impair the blood vessels’ ability to carry oxygen and vital nutrients to the heart muscle, ultimately putting users at a higher risk of heart complications.
However, the study also discovered a potential supplement that may help mitigate this risk. Genistein, a compound found in soy and fava beans, has shown promising results in reducing the harmful effects of THC on the blood vessels. Genistein has anti-inflammatory properties that can protect the blood vessels from damage and improve overall cardiovascular health.
While this research sheds light on the relationship between marijuana use and heart disease, it’s essential to note that more studies are needed to fully understand the extent of the risk and the potential benefits of genistein supplementation. In the meantime, individuals who use marijuana should be aware of the potential harm it may pose to their heart health and consider discussing their use with healthcare professionals.
Watch this video to have a greater understanding of the study:
THC and inflammation
THC, the psychoactive compound found in marijuana, has been found to promote inflammation in the body, which can ultimately lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This connection between THC and inflammation has raised concerns about the potential impact of frequent marijuana use on cardiovascular health.
The key to understanding this relationship lies in a receptor called CB1. CB1 receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system in the body, which is responsible for regulating various physiological processes. These receptors recognize endocannabinoids, which are naturally produced by the body, as well as cannabinoids like THC.
When THC enters the body, it can bind to CB1 receptors, leading to the activation of inflammatory pathways. This inappropriate activation of CB1 receptors by THC can result in a cascade of events that ultimately promote inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis.
Research has shown that chronic marijuana use can lead to higher levels of inflammatory markers in the bloodstream, indicating ongoing inflammation in the body. This chronic inflammation can damage the blood vessels and impair their ability to function properly, increasing the risk of cardiovascular issues such as heart disease and heart attacks.
It is important to note that while this link between THC, inflammation, and atherosclerosis is concerning, further research is needed to fully understand the complex relationship between marijuana use and cardiovascular health. In the meantime, individuals who regularly use marijuana may want to consider the potential impact on their heart health and speak with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
SOURCE: Skipina, T. M., Patel, N., Upadhya, B., & Soliman, E. Z. (2022). Relation of Cannabis Use to Elevated Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score. The American Journal of Cardiology, 165(1), 46-50.
How does chewing tobacco affect your health?
Chewing tobacco may seem like a less harmful alternative to smoking, but its health effects should not be underestimated. One of the most concerning aspects of chewing tobacco is its ability to cause nicotine addiction, just like smoking. This addiction can be incredibly difficult to break, leading to continued tobacco use and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Chewing tobacco also significantly increases the risk of several types of cancer. The habit has been linked to an increased risk of mouth, esophageal, and pancreatic cancers. These cancers can be life-threatening and require intensive treatment.
In addition to the risk of cancer, chewing tobacco can also lead to gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss. The habit exposes the gums and teeth to irritating substances, leading to inflammation and infection. Over time, this can cause gum disease, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
It’s important to note that the negative health effects of tobacco extend beyond chewing tobacco alone. Smoking tobacco, whether it be cigarettes or other forms, can also increase the risk of gum disease, tooth loss, and other oral health problems. Additionally, smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. It can also decrease the sense of smell and taste.
Overall, the health effects of chewing tobacco are serious and should not be taken lightly. If you or someone you know is using chewing tobacco, it is important to seek support and resources to quit and protect your health.
SOURCE: Smokeless tobacco products. Mayo Clinic.
SOURCE: Gum disease and heart disease: The common thread. Harvard Health Publishing.
Is Vaping Safer Than Smoking a Cigarette?
Vaping has gained popularity in recent years as a perceived safer alternative to traditional cigarette smoking. While it is true that vaping eliminates the harmful effects of tobacco smoke, it is important to understand that it is not without risks.
E-cigarettes, or vapes, contain a liquid that is heated and vaporized for inhalation. This liquid often contains high levels of nicotine, the addictive substance found in cigarettes. The high nicotine content in e-cigarettes can lead to addiction, especially among young people who may be more vulnerable to its effects. Additionally, the chemicals used to flavor vape liquids can be harmful to the lungs, leading to severe lung damage over time.
It’s also important to remember that while vaping may be a less harmful option for those who are trying to quit smoking, it is not an entirely safe habit. Vaping has been associated with an increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular problems, as well as potential lung injuries.
On the other hand, cigarette smoking is well-known for its detrimental effects on health. Tobacco smoke contains thousands of harmful chemicals, including tar, carbon monoxide, and formaldehyde. These chemicals can lead to a wide range of health problems, including lung cancer, heart disease, respiratory infections, and even premature death.
While vaping may be perceived as a safer alternative to smoking cigarettes, it is crucial to understand that it is not risk-free. Both vaping and smoking have their own set of potential dangers and health risks. Quitting smoking altogether remains the best way to protect your health and reduce your risk of developing serious medical conditions.
SOURCE: Alzahrani, T., Pena, I., Temesgen, N., & Glantz, S. A. (2018). Association Between Electronic Cigarette Use and Myocardial Infarction. American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
How are health problems from tobacco diagnosed?
When it comes to diagnosing health problems caused by tobacco use, healthcare providers use various methods to assess the extent of the damage and determine the appropriate treatment. Understanding the specific tests and examinations used can help individuals who have been affected by tobacco-related health problems.
Depending on the symptoms and type of tobacco use, healthcare providers may use tests such as lung function tests, chest X-rays, and computed tomography (CT) scans. Lung function tests can evaluate how well the lungs are functioning and help identify conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Chest X-rays and CT scans can provide detailed images of the lungs, helping to detect signs of lung cancer or other respiratory issues.
However, it’s important to note that discussing tobacco use history with the healthcare provider is crucial during the diagnostic process. Sharing information about the duration and intensity of tobacco use can provide valuable insights into the potential health risks and aid in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Tobacco-related health problems can be diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, medical history evaluation, and diagnostic testing. Engaging in open and honest conversations with healthcare providers allows for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized approach to manage the effects of tobacco use.
What other conditions may be caused or worsened by tobacco?
In addition to the well-known dangers of smoking, such as lung cancer and respiratory diseases, tobacco use can also have a detrimental effect on various other aspects of our health. Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease as it increases the risk of developing conditions such as heart attack, stroke, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and diabetes.
Smoking damages the blood vessels and reduces blood flow, making it easier for blood clots to form. This can lead to heart attacks and strokes, which occur when blood supply to the heart or brain is blocked. Furthermore, smoking causes the build-up of fatty plaque within the coronary arteries, increasing the risk of coronary artery disease. Similarly, peripheral artery disease occurs when plaque builds up in the peripheral arteries, often in the legs and feet, leading to reduced blood flow to these areas.
Tobacco use also increases the risk of developing diabetes, as smoking impairs insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation in the body. Smokers are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to non-smokers.
Additionally, smoking has other negative effects on our health, including decreased levels of HDL (good) cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, erectile dysfunction, gum disease, and various lung diseases.
It is crucial to recognize the broader impact of tobacco use on our health beyond just the lungs. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risks of these conditions and improve overall health.
Diabetes and Heart Disease: A Deadly Connection
Diabetes and heart disease have a deadly connection that puts individuals at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and stroke. When diabetes is poorly managed, it can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and impact the heart’s ability to function properly.
In addition to the direct effects on blood vessels, conditions associated with diabetes further contribute to the risk of heart disease. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is common among people with diabetes and significantly increases the likelihood of heart complications. Similarly, high cholesterol levels, often seen in individuals with diabetes, can lead to the build-up of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart and increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Obesity and inactivity, which are often linked to diabetes, also play a role in worsening heart disease risk. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, while a sedentary lifestyle weakens the cardiovascular system. These factors combined create a perfect storm for heart problems.
Fortunately, individuals with diabetes can take steps to reduce their risk of heart disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing blood sugar levels through medication or insulin therapy. It is essential to control high blood pressure and cholesterol levels through medication, as well as regularly monitoring them.
By addressing these risk factors and adopting healthy habits, those with diabetes can greatly reduce their chances of developing heart disease and live a longer, healthier life. Remember, prevention and management are vital in fighting against the deadly connection between diabetes and heart disease.
SOURCE: Diabetes and Your Heart. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
SOURCE: Smoking and Diabetes | Overviews of Diseases/Conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Smoking affects so much more than your lungs. It can impact your vascular health, your dental health, and your mental health. Smoking can cause diabetes, depression, gum disease, and hypertension. It can lead to a sedentary lifestyle. Whether it be a cigarette, a vape, or marijuana, smoking can impact the way your blood vessels function and the flexibility of your arteries. Every single one of these changes increases a person’s risk of heart disease. With heart disease being the leading cause of death for women and men in the United States and smoking having the title of the leading cause of preventable disease, disability, and death, it’s not difficult to see that they are connected.
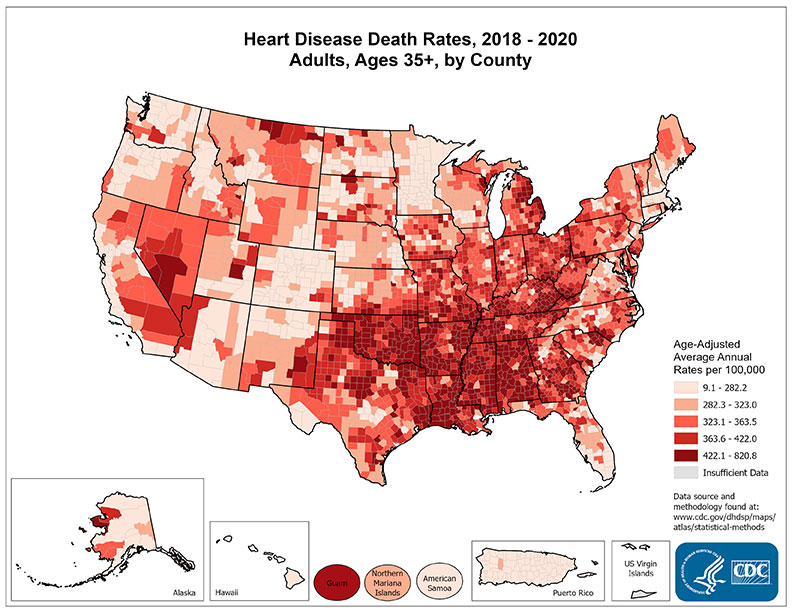
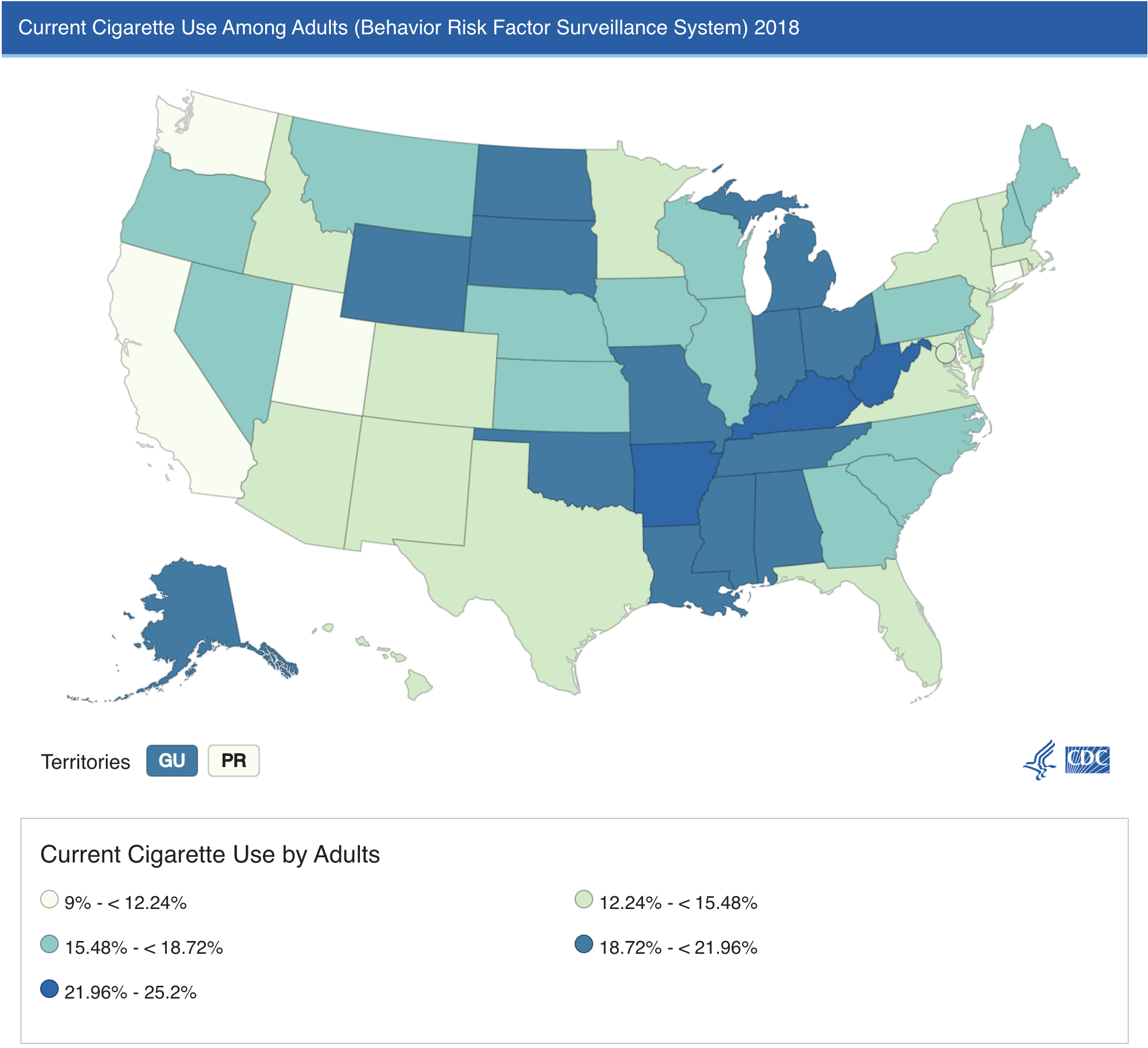
Compare the two maps below:
SOURCE: Current Cigarette Smoking Among Adults in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
SOURCE: Heart Disease Death Rates, Total Population Ages 35+1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
By having a deeper understanding of the damaging effects of smoking, we hope that you and your loved ones can find the motivation to quit smoking. It just might save your life!
Most people associate cigarette smoking with breathing problems and lung cancer. But smoking harms nearly every organ in the body, including the heart, blood vessels, lungs, eyes, mouth, reproductive organs, bones, bladder, and digestive organs. Smoking is the main preventable cause of death and illness in the United States. Cigarettes, cigars, e-cigarettes, pipes and chewing tobacco kill over 480,000 Americans per year. Of these, 41,000 deaths were attributed to secondhand smoke exposure. No level of tobacco use is found to be safe
The nicotine from chewing tobacco or any amount of smoking, even light smoking or occasional smoking, can damage your heart and blood vessels, temporarily raise blood pressure and lower your exercise tolerance. This damage increases your risk of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up in the arteries. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows your arteries. Smoking also decreases the amount of oxygen that the blood can carry and increases the tendency for blood to clot. Blood clots can form in arteries causing a range of heart diseases that could ultimately result in a stroke or sudden death.
A person’s chance of heart disease increases with the number of cigarettes they smoke and how long they have smoked. If you smoke a pack of cigarettes a day, you are twice as likely to have a heart attack as someone who doesn’t smoke. For women who take birth control pills and people who have diabetes, smoking poses an even greater risk to the heart and blood vessels. Chewing tobacco, e-cigarettes, and the smoke from cigars and pipes contains the same harmful chemicals as the smoke from cigarettes and can result in heart disease.
The impact of tobacco smoke is not confined solely to smokers. When you smoke, the people around you, especially children, are also at risk for having health problems. Secondhand smoke is the smoke that comes from the burning end of a cigarette, e-cigarette, cigar, or pipe or the smoke that’s breathed out by a person who is smoking. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals that people inhale when they smoke. Secondhand smoke can damage the hearts and blood vessels, and can increase the risk of heart attack and death, in people who don’t smoke in the same way that active smoking harms people who do smoke. About 35,000 nonsmokers die from heart disease each year as a result of exposure to secondhand smoke.
The good news is that quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke can help reverse heart and blood vessel damage and reduce heart disease risk. The impact of quitting is almost immediate
- Within 20 minutes of quitting smoking, blood pressure and pulse return to normal, and circulation improves.
- Within eight hours, blood oxygen levels increase and the chances of a heart attack start to fall.
- Within 24 hours, carbon monoxide is eliminated from the body and the lungs start to clear out mucus and debris.
- Within 72 hours, the lungs can hold more air and breathing becomes easier.
- Within five years, the risk of a heart attack falls to about half that of a smoker.
- Within 10 years, the risk of lung cancer falls to around half that of a smoker.
- Within 15 years, the risk of heart disease becomes nearly the same as someone who has never smoked.
- Quitting when older is still worthwhile: among smokers who quit at age 66 years, men gained up to two years of life, and women gained up to 3.7 years.
Quitting smoking is possible, but it can be hard. Millions of people have quit smoking successfully and remained nonsmokers. A variety of strategies, programs, and medicines are available to help you quit smoking. Above all, you must also want to quit smoking for yourself, and not try to quit to please your friends or family.
- First, pick a date to stop smoking and then stick to it.
- Write down your reasons for quitting. Read over the list every day, before and after you quit.
- Write down when you smoke, why you smoke, and what you are doing when you smoke. You’ll learn what causes you to smoke.
- Stop smoking in certain situations (such as during your work break or after dinner) before actually quitting.
- Make a list of activities you can do instead of smoking — and do them when the urge hits.
- Ask your doctor about nicotine gum or patches, or drugs that can help you quit.
- Join a stop-smoking support group or program.
If you relapse, don’t lose hope. Seventy-five percent of those who quit smoke again. Most folks quit three times before they succeed. Plan ahead and think about what you’ll do the next time you get the urge to smoke.